The text below is an advertorial article that was not written by Cryptonews.com journalists.

‘Metaverse’ may sound like an exotic term, but not for long. In the near future, we all will interact, work, dance, data (and sometimes shoot at the bad guys) in a mind-boggling hybrid space at the intersection of the latest technologies, from VR to blockchain.
Why ‘meta’?
‘Meta’ means ‘beyond’ in Greek. The word metaverse appeared for the first time in Neal Stephenson’s cult novel Snow Crash, which came out in 1992. In the novel, people spend all their time in a virtual space interacting as 3D ‘avatars’. They frequent 3D bars and clubs, conduct business affairs, etc. The novel’s metaverse is a sort of Web 2.0 (by the way, the internet had already existed for 10 years when the Snow Crash was published).
Stephenson’s idea wasn’t unique: similar concepts of alternative virtual universes popped up many times in the cyberpunk community of the late 80s and early 90s. But it was the memorable word metaverse that caught on.
Now, almost thirty years later, we are finally witnessing the metaverse being born – not in a sci-fi book but in reality. Some of the key participants acknowledge that they were inspired by Neal Stephenson’s idea: for example, the lead developer at Oculus VR Michael Abrash at some point to embody this concept in the iconic multiplayer shooter Quake.
The 7 core technologies of the metaverse
The metaverse is a hybrid reality that goes beyond both our physical world and the virtual world. It’s not an imaginary space, like the one in The Matrix, but rather an intricate nexus that produces powerful synergy. The development of the metaverse relies on a number of pioneering technologies.
1) VR/AR/XR
Even though VR (virtual reality) plays the key role, augmented and mixed reality are also very important for the metaverse, for two reasons:
- The number of VR headset owners is still low, so metaverse projects must ensure cross-platform support if they wish to attract a wide audience – and AR is already supported on most new flagship smartphones.
- The current VR headset models aren’t always suitable for spending a lot of time in the virtual world: after a while, some users begin to feel fatigue and discomfort.
2) 5G
Multiplayer virtual reality requires very fast data transfers, and WiFi alone won’t do the trick. With 4G, we got used to watching YouTube videos on the bus; and with the arrival of 5G, it will become just as normal to connect to a VR meeting while commuting to work, for example.
3) WebVR
This technology allows users to access VR content directly in the browser, without installing any heavy apps. Google, Oculus, and Microsoft have shown support for WebVR. Without this tool it would be hard to implement a large-scale metaverse. WebVR, for its part, needs 5G: without fast internet, web apps tend to lag and freeze.
4) Blockchain
You’ll be able to shop for goods and services in the metaverse just as easily as you now do it in social media. The difference is that those goods will be mostly virtual: clothes for avatars, for example. Most payments will be made in tokens as the most ‘virtual’ type of money. For example, the Sensorium Galaxy digital metaverse is already implementing a native SENSO token as a way to pay for tickets to virtual concerts, avatars and accessories, etc.
5) AI
The metaverse will be populated not just by the avatars of real users but also by computer-generated NPCs (non-playing characters). Apart from functioning as the crowd in the background, they’ll be able to sustain a simple chat thanks to a special machine learning algorithm that powers them. And the more advanced these AI algorithms become, the more natural and complex the behavior of NPCs will be. For example, Sensorium Galaxy NPCs talk and act so realistically that you’ll even be able to go on dates with them.
6) Gaming engines
The 3D graphics for the leading VR projects is made using the same engines as the best computer games. The best-known is Unreal Engine by Epic Games, the studio behind Fortnite. Its technology allows to obtain realistic textures, lighting, and everything else that’s needed to create an illusion of presence.
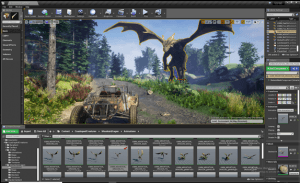
7) Motion tracking
As users embark on more and more complex activities in VR, their avatars have to repeat their motion with precision, down to the movements of the fingers. Dance, sports, drawing, music – all these activities require tracking a lot of points on that body, and that means either using a lot of sensors or a more advanced technology.
Precise motion tracking will also help eliminate physical and psychological discomfort when wearing a VR headset for a long time.
What can you do in the digital metaverse?
In a few words, anything you like! And while you can’t eat or drink in the virtual space, nothing stops you from sitting down over a cocktail and chatting (or even flirting) with an attractive avatar. By the way, that’s how dating works on a starship in Sensorium Galaxy (watch
mobile app teaser).
Here are just some of the possible activities – and various VR teams are already working on many of them:
- Concerts by celebrity musicians (with the performer present as an avatar);
- Discos and nightclubs;
- Lessons
- Sports, both amateur and competitions. This type of activity is harder to implement, because it requires precise motion tracking and zero lag between the movements of the physical body and those of the avatar. But this issue, too, will surely be resolved in the future;
- Movies – think of the special effects you can add to the experience of watching a film a virtual space;
- Theater and performances;
- Dating;
- Meeting with friends and family who live far away. This is much better than video calls, though ideally you’d need hyper-realistic avatars that look exactly like real people (Codec Avatars is one project working on this);
- Business meetings, negotiations, and conferences;

- Trade fairs and product presentations;
- Museums and art galleries, plus creating new works, such as virtual street art;
- Shopping: an avatar needs a lot to live comfortably – a wardrobe, accommodation, means of transportation, etc. And since the metaverse isn’t bound by the physical laws of our world, a house can float in the air, and you could move around riding a dragon;
- Advertising: marketing specialists can have a field day in the metaverse. It has unlimited space for placing billboards, sponsorship deals, PR events, etc.
One metaverse or many?
Just like the history of aviation began with several independent inventors and their planes, the era of metaverses will likely begin with several independent platforms. The next step will be to develop a way to move between metaverses without taking off your VR headset. In the WebVR community this is called deep linking, as an analogy with deep links that let users access one app from another.
Yet another interesting concept is ‘VR backpacks’ – a way to carry objects from one virtual space to another. The idea is that your avatar’s clothes and other belongings should move with you when you teleport to another metaverse. It’s logical: once you spend real money on in-platform artifacts, you want to be able to use them all the time. Backpacks will probably use the NFT (non-fungible token) technology: these are special blockchain tokens that encode unique digital objects.
However, the ultimate goal is to merge all the metaverses into one. You could describe it as a virtual universe composed of galaxies created by different developers. Some of them will be highly realistic, while others will look cartoonish; some will explore futuristic themes, while others will have fantasy environments and plots similar to The Lord of the Rings. Some will serve as spaces for business or research, and others will be dedicated to entertainment. This variety is what gives the metaverse its huge potential.
The two metaverses you can experience right now
Fortnite
In December 2019, Epic Games CEO Tim Sweeney was asked on Twitter if he thinks Fortnite is a game of a platform. His response was cryptic: ‘Fortnite is a game. But please ask this question again in 12 months.’
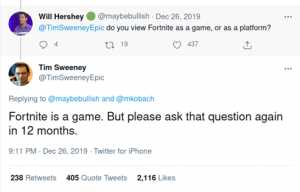
Indeed, although Fortnite doesn’t use VR (yet), it has many other features of a metaverse, for example:
– In April 2020, Fortnite hosted a virtual concert by the famous hip hop artist Travis Scott, who played it as an avatar;

– To mark the release of the latest Star Wars film, there was a presentation attended by the director JJ Abrams (as an avatar) and even Emperor Palpatine himself;
– Players spend hundreds of millions of dollars every year to buy in-game items with the internal currency, V-backs;
– The game features a multitude of sponsored integrations, mostly as skins of celebrities, movie characters, and even characters from other computer games;
– Movie trailers and whole films are already streamed in Fortnite;

– Apart from shooting at enemies, players spend a lot of time hanging out.
Sensorium Galaxy
Sensorium Galaxy is a digital metaverse in the full sense of the word – with lots of exotic worlds and an active use of VR. The developers are betting on highly realistic 3D graphics (made using Unreal Engine) and an advanced AI that powers NPCs.

It’s worth noting that Sensorium Galaxy is a multiplatform solution, so those who don’t have an Oculus headset will still be able to interact with other avatars, buy avatars with SENSO tokens, etc.
The first world to be launched, in a few months from now, is called PRISM (watch the video teaser). The main theme is electronic music: Sensorium Galaxy has already signed contracts with a number of famous artists, including David Guetta (the list can be found here). You’ll be able to watch their concerts in otherworldly VR clubs using a computer or, even better, teleport to the club using a VR headset to fully experience the concert together with other avatars.

The second world is MOTION, dedicated to mindfulness and located underwater. You can watch the highly detailed trailer here.
The main way to pay for concert tickets, avatar accessories, merchandise signed by the musicians, and other premium content is the native SENSO tokens. They give a 20% discount off the full price (that is, the price you’ll pay if using a bank card). SENSO is already available on several crypto exchanges: KuCoin, Poloniex, Bittrex etc.
The metaverse isn’t a theory or a futuristic forecast – it’s our imminent future. The arrival of metaverses will produce a grandiose transformation in society, similar to the impact of the internet. And knowing that we’ll be direct participants in this transformation is endlessly exciting.
Credit: Source link